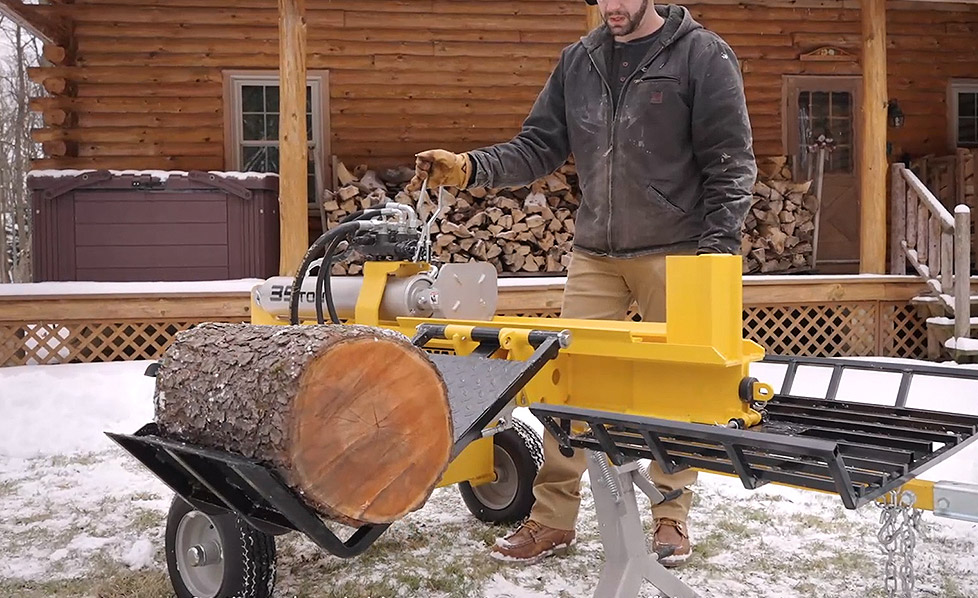
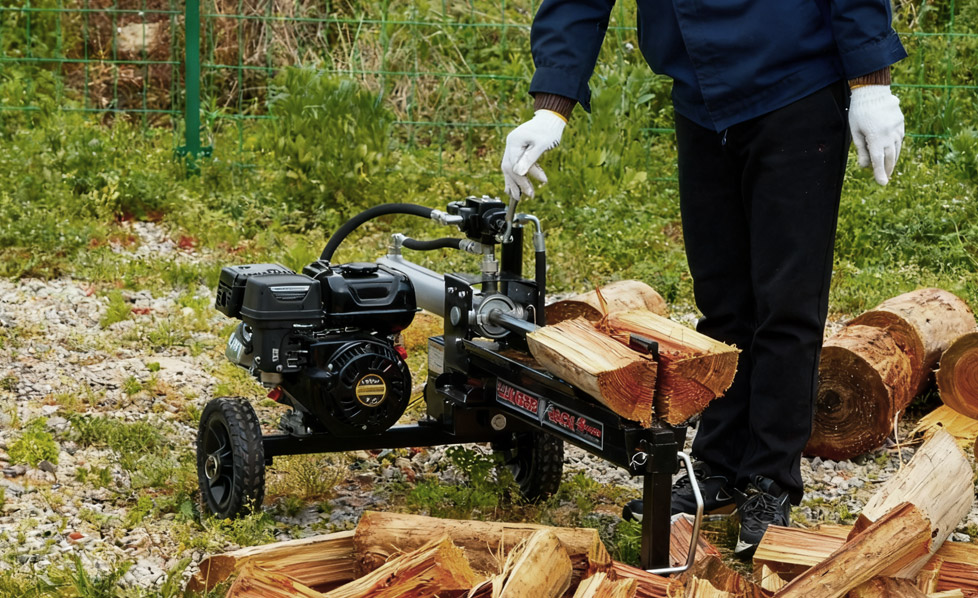
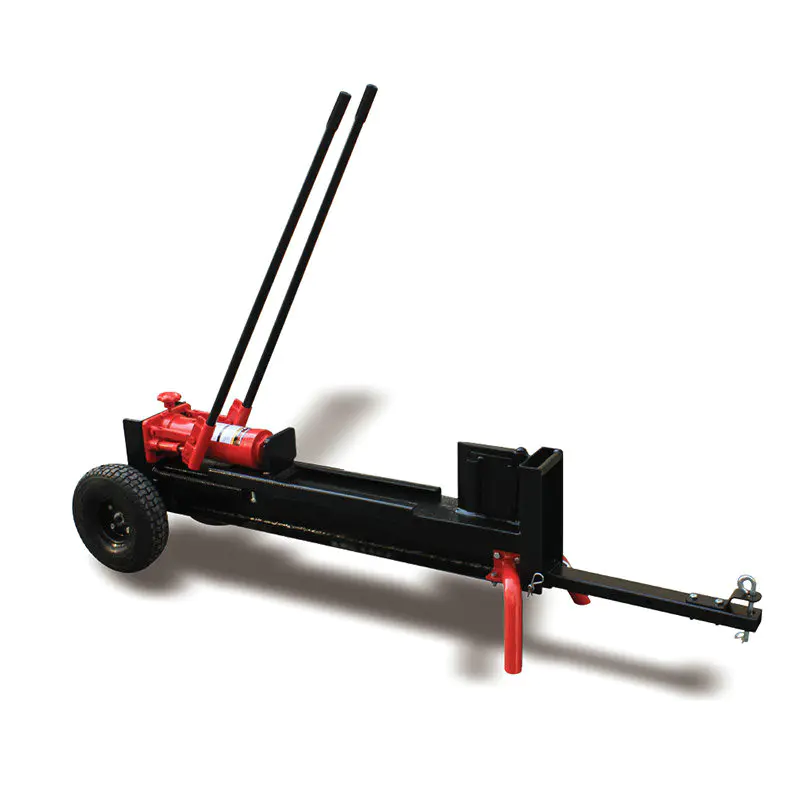
● Horizontal operation position only● 17” Hardened steel wedge● 21.6”/...
See Details
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Industry News
Our Footprints Are Around The World
We provide quality products and services to customers from all over the world.
We provide quality products and services to customers from all over the world.
Search
Categories
What Affects the Splitting Power of an Electric Log Splitter?
The splitting power of an electric log splitter is a crucial factor in determining its effectiveness and efficiency when splitting logs. Several key factors influence the splitting power of an electric log splitter, and understanding them can help you choose the right machine for your specific needs. Here are the primary factors that affect the splitting power of an electric log splitter:
Motor Power:
The electric motor is the heart of an electric log splitter, and its power rating is one of the most significant factors affecting splitting power. Motor power is typically measured in watts (W) or horsepower (HP). A higher motor power rating generally results in greater splitting force.
For smaller electric log splitters designed for residential use, motor power typically ranges from 1 HP to 3 HP. Commercial-grade models may have motors with higher power ratings, exceeding 5 HP.
Hydraulic System:
The hydraulic system in an electric log splitter plays a critical role in generating the force needed to split logs. A powerful hydraulic system can significantly impact the machine's splitting power.
Look for log splitters with robust hydraulic pumps and cylinders. The pump's flow rate and the cylinder's size and pressure rating are key factors that affect the hydraulic force.
Splitting Force:
The splitting force is often expressed in tons and is a direct measure of the log splitter's power. Higher splitting force means the machine can handle larger and tougher logs.
Electric log splitters typically offer splitting forces ranging from 5 tons for smaller models to 25 tons or more for heavy-duty commercial units.
Log Length Capacity:
The length of the logs you plan to split can also impact the effectiveness of the log splitter. If you often work with longer logs, ensure that the machine's design accommodates them.
Longer logs may require a higher splitting force to ensure consistent and efficient splitting.
Ram Speed and Cycle Time:
Ram speed refers to how quickly the splitting wedge moves through the log. A faster ram speed can improve efficiency by reducing the time it takes to split a log.
Cycle time is the total time it takes for the log splitter to complete a splitting cycle, including splitting the log and returning to its starting position. Shorter cycle times can enhance productivity.
Wood Type and Density:
The type of wood you are splitting and its density can also affect the splitting power required. Hardwoods like oak and hickory may require more force to split than softer woods like pine.
Consider the types of wood you'll be working with to ensure that your log splitter has the appropriate splitting force.
Machine Design and Construction:
The overall design and build quality of the log splitter can influence its splitting power. Sturdy construction and durable components are essential for maintaining consistent power and performance.
In conclusion, the splitting power of an electric log splitter is influenced by factors such as motor power, hydraulic system capabilities, splitting force, log length capacity, ram speed, cycle time, wood type, and machine design. When choosing an electric log splitter, carefully assess your specific needs and the types of logs you plan to split to select a machine with the appropriate power and features for efficient and effective log splitting.
PREV:How does a Gas Log Splitter-Dual Action Acting work?
NEXT:What site preparation is required when using a stump grinder?
NEXT:What site preparation is required when using a stump grinder?
Interested in cooperation or have questions?
Related products
-

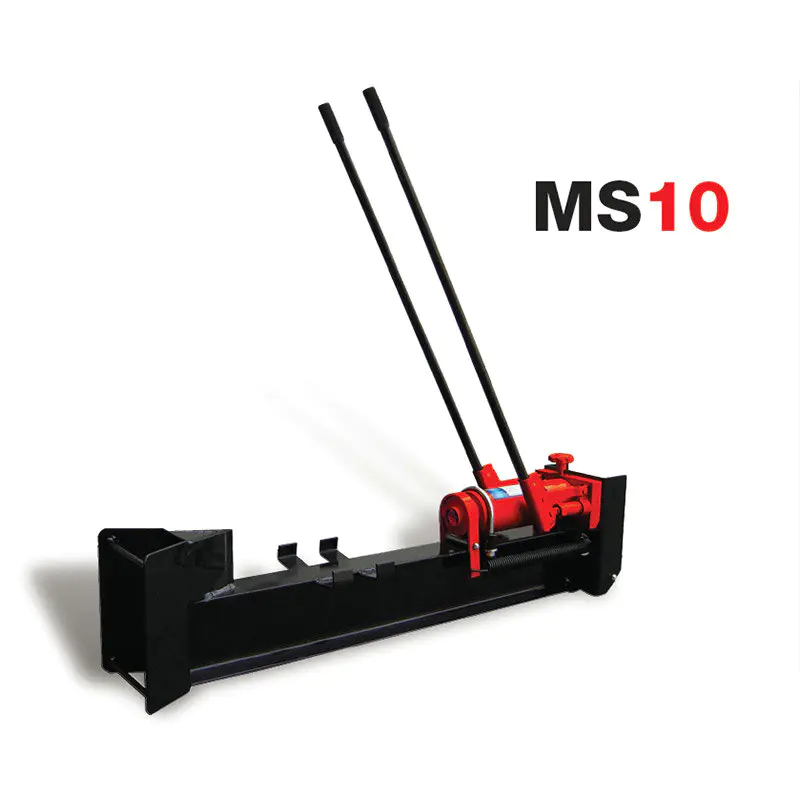
● Horizontal operation position only● Hardened steel wedge● Steel log ...
See Details -

● Vertical operation position only ● Hardened steel wedge ● 24” / 61cm...
See Details -
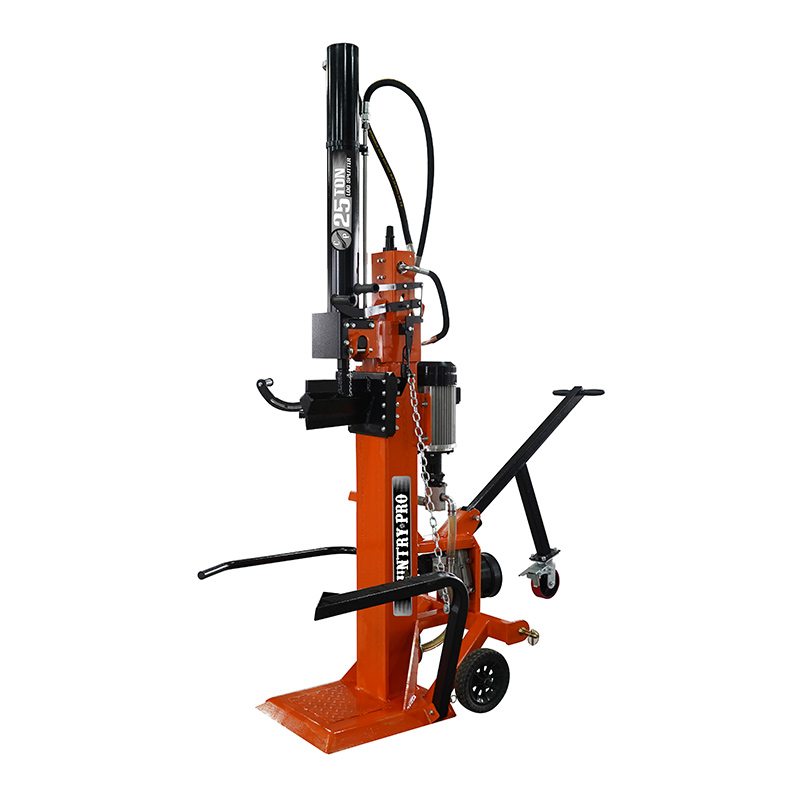

Vertical operation position onlyHardened steel wedge43.3” / 110cm log ...
See Details

 LANGUAGE
LANGUAGE English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Français
Français























