DESCRIPTION ♦Spread for fertilizer, grass seeds, salt ♦A...
See Details
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Home / News / Industry News / How does the chipper shredder's engine power affect its performance when dealing with larger branches and debris?
Industry News
Our Footprints Are Around The World
We provide quality products and services to customers from all over the world.
We provide quality products and services to customers from all over the world.
Search
Categories
How does the chipper shredder's engine power affect its performance when dealing with larger branches and debris?
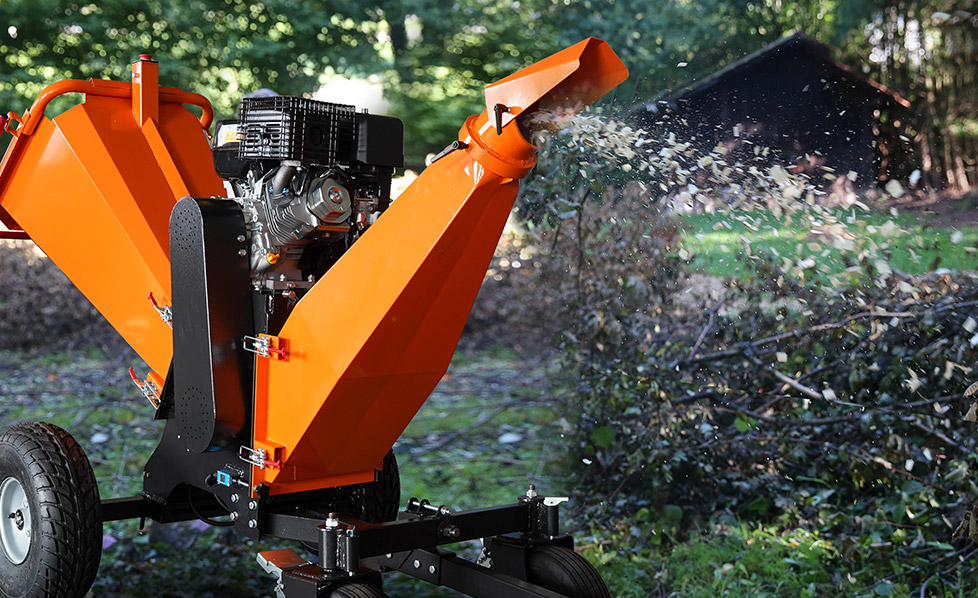
The engine power of a chipper shredder is a critical factor that significantly affects its performance when dealing with larger branches and debris. This power determines the chipper shredder's ability to efficiently process, chip, and shred substantial pieces of wood and other yard waste. In this comprehensive explanation, we will delve into the intricate relationship between engine power and performance in chipper shredders, highlighting the ways in which engine power influences the machine's effectiveness in handling more substantial materials.
A chipper shredder is a versatile yard tool designed to reduce bulky organic materials such as branches, leaves, and twigs into smaller, more manageable pieces. These machines play a vital role in residential and commercial landscaping, aiding in waste reduction, composting, and overall property maintenance. When it comes to dealing with larger branches and debris, the engine power of a chipper shredder becomes paramount.
Engine Power and Cutting Mechanism:
At the heart of a chipper shredder's ability to process larger branches and debris is its cutting mechanism. Most chipper shredders utilize a combination of sharp blades or knives that rotate at high speeds to cut, chip, and shred the input material. The engine power directly affects the performance of these cutting mechanisms in multiple ways.
Higher engine power translates to greater torque, which is the rotational force generated by the engine. This torque is crucial for driving the cutting blades through dense and robust materials. When dealing with larger branches, the cutting blades need sufficient torque to effectively penetrate the material's surface and make clean cuts. Inadequate torque can lead to the machine getting stuck or jammed, reducing efficiency and potentially causing damage to the chipper shredder.

Efficient Processing of Larger Material:
Larger branches and debris often have thicker and more rigid structures compared to smaller materials like leaves and twigs. The engine power directly influences the chipper shredder's ability to break down these larger materials into smaller, more manageable pieces. A more powerful engine enables the cutting blades to slice through the material with greater ease, reducing the risk of clogs and jams.
Moreover, the rotational speed of the cutting blades, which is directly linked to the engine power, determines how quickly the machine can process the input material. Higher engine power allows for faster blade rotation, leading to a more efficient feed rate. This means that the chipper shredder can process larger branches and debris more quickly, contributing to improved productivity and reduced overall processing time.
Preventing Clogs and Downtime:
One of the challenges when dealing with larger branches and debris is the potential for clogs within the chipper shredder's mechanism. An underpowered machine might struggle to process larger materials, leading to blockages in the chute or cutting chamber. Clogs not only reduce efficiency but also require manual intervention to clear, leading to downtime and interruptions in the work process.
A chipper shredder with ample engine power can power through larger branches without getting bogged down, minimizing the risk of clogs. The cutting blades can maintain their momentum and effectiveness, ensuring a consistent and uninterrupted processing flow.
Balancing Engine Power and Design:
While engine power is a crucial factor, it's important to note that the chipper shredder's overall design and engineering also play a significant role in its performance. The design of the cutting chamber, the arrangement of blades, and the efficiency of the discharge system all contribute to how effectively the chipper shredder can handle larger branches and debris.
A well-designed chipper shredder takes into account the engine power, the size and angle of the feeding chute, and the spacing and sharpness of the blades. These elements work in harmony to ensure that the machine can effectively process larger materials without compromising safety, efficiency, or the integrity of the machine's components.
In conclusion, the engine power of a chipper shredder is a critical factor that directly impacts its performance when dealing with larger branches and debris. A more powerful engine provides the necessary torque and rotational speed to enable the cutting blades to penetrate, chip, and shred thicker and denser materials efficiently. It reduces the risk of clogs, enhances processing speed, and contributes to overall productivity.
However, it's important to remember that engine power is just one aspect of a chipper shredder's performance. The machine's design, blade quality, and other features also influence its ability to handle larger materials effectively. When selecting a chipper shredder for handling substantial branches and debris, it's essential to consider a balance between engine power and overall design to ensure optimal performance and durability.
PREV:What safety features does the Red Rock log splitter offer to ensure the operator's protection during log splitting operations?
NEXT:What are the key safety features to consider when using a gasoline log splitter?
NEXT:What are the key safety features to consider when using a gasoline log splitter?
Interested in cooperation or have questions?
Related products
-

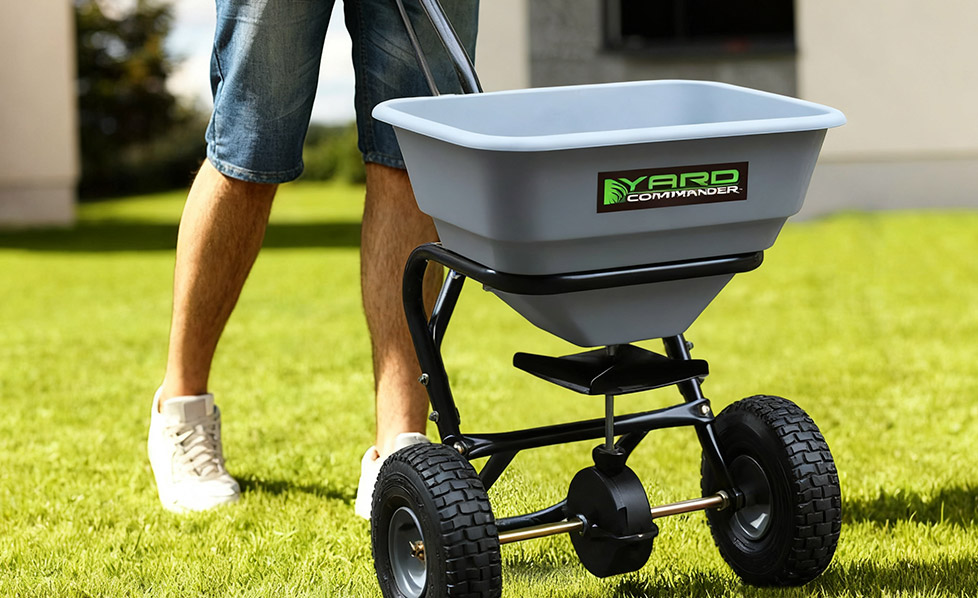
DESCRIPTION ♦All purpose spreader ♦Accessories: screen &...
See Details -

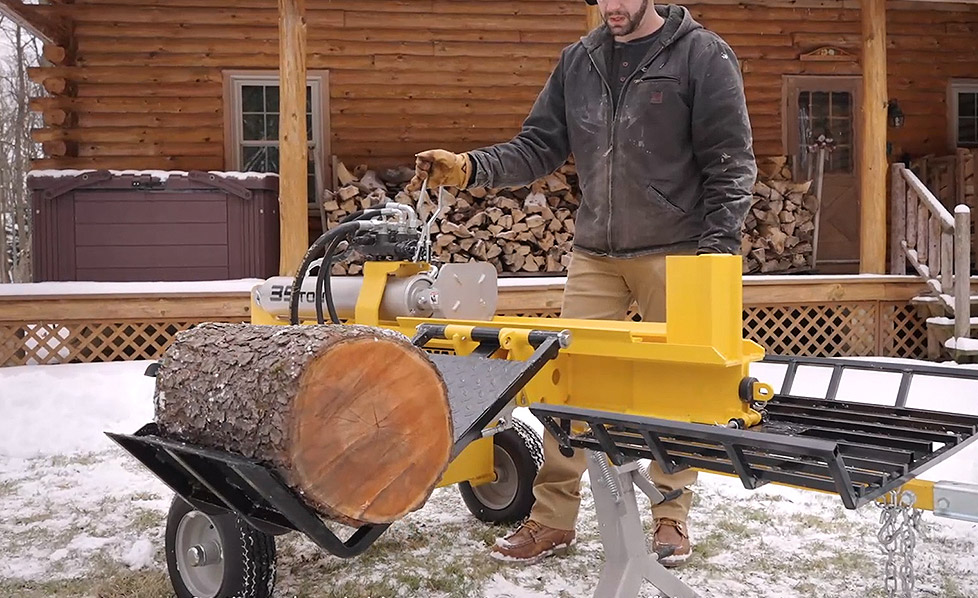
DESCRIPTION Accommodates splitting in horizontal only Half beam design...
See Details -

Vertical or horizontal operating position lets you work most efficien...
See Details -

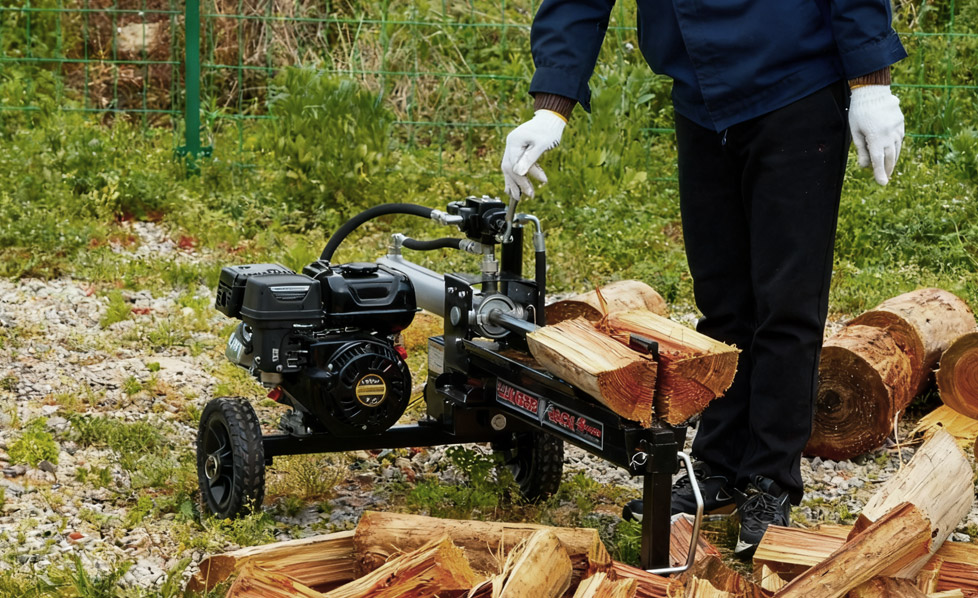
If you regularly split wood, the 32ton log splitter will save you tim...
See Details -

DESCRIPTION Working at horizontal position onlyAuto return hydraulic c...
See Details

 LANGUAGE
LANGUAGE English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Français
Français





















