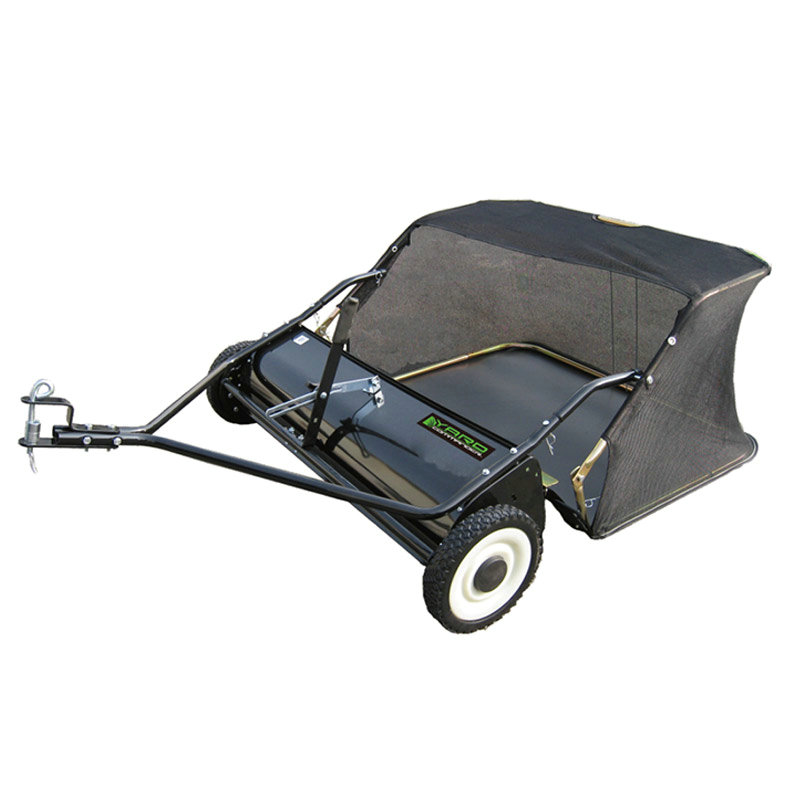
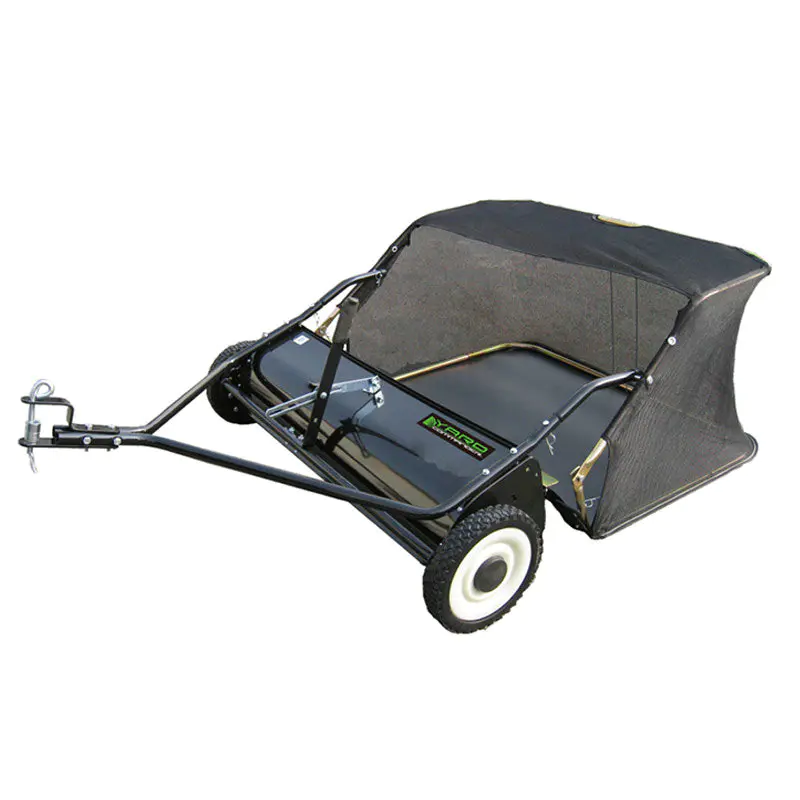
DESCRIPTION ♦Heavy-duty puncture proof steel roller ♦Eas...
See Details
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
We provide quality products and services to customers from all over the world.
Content
- 1 Overview of Push Lawn Sweepers
- 2 Design Differences Between Manual and Self-Propelled Push Lawn Sweepers
- 3 Operational Efficiency and Performance
- 4 Maintenance Considerations
- 5 Ergonomics and User Experience
- 6 Suitability for Different Lawn Conditions
- 7 Environmental and Cost Considerations
- 8 Common Challenges and Solutions
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 FAQ
- 11 References
What are the differences between manual and self-propelled push lawn sweepers?
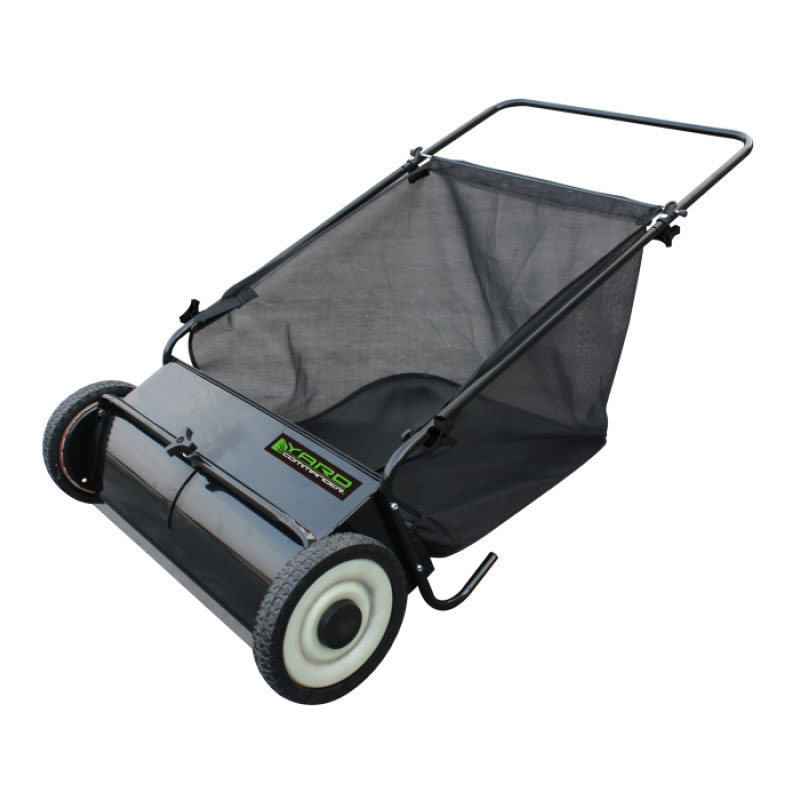
Maintaining a well-kept lawn requires attention to detail and the use of efficient tools. Among the essential equipment for lawn care, the push lawn sweeper plays a critical role in collecting leaves, grass clippings, and other debris. These devices provide a cleaner and healthier lawn environment, reducing the need for chemical treatments and manual labor. While various types of lawn sweepers exist, manual push lawn sweepers and self-propelled push lawn sweepers represent two primary categories that buyers encounter. Understanding the differences between these two types is essential for selecting the appropriate equipment for specific lawn conditions and user requirements.
Overview of Push Lawn Sweepers
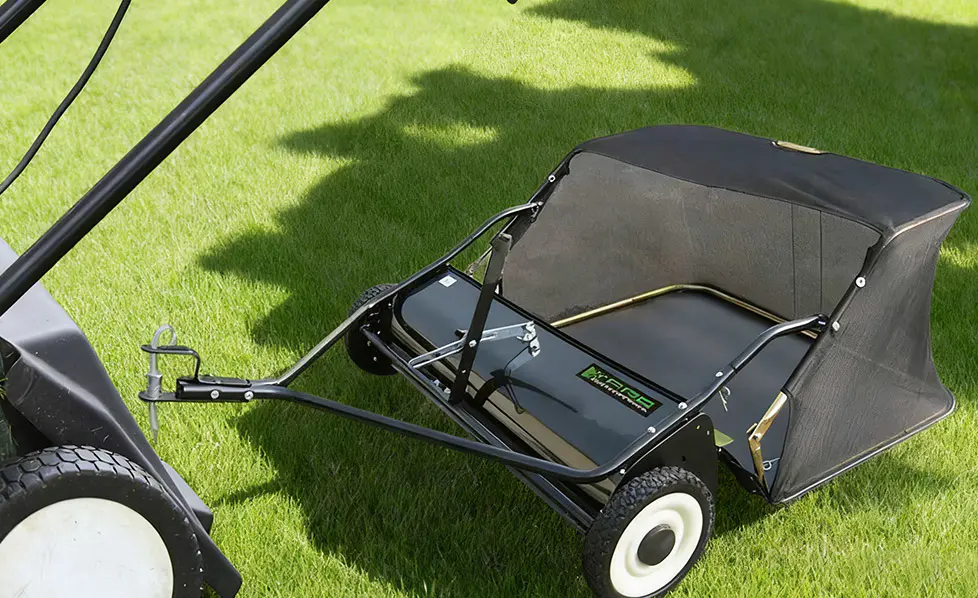
A push lawn sweeper is a mechanical device designed to collect debris from lawns through rotating brushes that sweep material into a collection hopper. These sweepers are typically equipped with adjustable brushes, wheels that facilitate smooth motion, and detachable collection bags for easy disposal of collected material. The primary distinction between manual and self-propelled versions lies in their operational mechanics and power assistance. While manual sweepers rely entirely on human propulsion, self-propelled sweepers incorporate a mechanism that assists movement, reducing physical exertion. Both types are widely used in residential and light commercial landscaping, though their selection often depends on the size of the lawn, terrain complexity, and user capability.
Design Differences Between Manual and Self-Propelled Push Lawn Sweepers
Manual push lawn sweepers are generally characterized by a straightforward and lightweight design. The frame is typically made from steel or reinforced plastic, and the brushes rotate through the motion of the wheels as the user pushes the sweeper. The simplicity of their construction ensures lower initial cost, easier storage, and straightforward maintenance.
In contrast, self-propelled push lawn sweepers incorporate a drivetrain mechanism that assists with forward movement. This mechanism is usually connected to the rear wheels and may include gear systems or friction drives that enhance motion without requiring constant human force. While the basic sweeping function remains similar to that of manual versions, self-propelled sweepers offer additional features such as variable speed control and enhanced wheel traction, which improve performance on uneven or sloped terrain.
Table 1: Key Design Features Comparison
| Feature | Manual Push Lawn Sweeper | Self-Propelled Push Lawn Sweeper |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight, easier to lift | Heavier due to drivetrain |
| Frame Material | Steel or reinforced plastic | Steel or reinforced plastic |
| Operational Mechanism | Entirely human-powered | Assisted by drive mechanism |
| Speed Control | Dependent on user strength | Variable or automatic speed |
| Terrain Adaptability | Best for flat or gently sloped lawns | Suitable for uneven or sloped lawns |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
The table above highlights the primary design distinctions, which influence usability, suitability, and performance. Buyers who prioritize affordability and simplicity may prefer manual models, whereas those seeking efficiency on larger or more complex lawns may consider self-propelled options.
Operational Efficiency and Performance
The operational efficiency of a push lawn sweeper depends on brush design, wheel mechanics, and user interaction. In manual sweepers, the force applied by the user directly affects the speed and brush rotation. While this provides precise control over delicate areas, it can limit the area coverage rate, especially for larger lawns. Brush engagement in manual sweepers is fully dependent on wheel movement; if the user moves too slowly, collection efficiency decreases.
Self-propelled sweepers mitigate these limitations by incorporating a mechanical assist. The drive system ensures consistent forward motion, allowing brushes to operate at optimal speed regardless of user strength. This results in higher debris collection efficiency, particularly in dense leaf conditions or on lawns with moderate slopes. Additionally, self-propelled sweepers often feature larger hopper capacities or multiple brush systems, further improving performance and reducing the frequency of emptying collected material.
Table 2: Operational Efficiency Comparison
| Parameter | Manual Push Lawn Sweeper | Self-Propelled Push Lawn Sweeper |
|---|---|---|
| Area Coverage Rate | Moderate, user-dependent | High, consistent |
| Debris Collection Efficiency | Moderate, variable | High, consistent |
| Brush Speed Control | Manual adjustment only | Mechanically assisted |
| User Fatigue | High on large lawns | Reduced due to drive assistance |
| Suitable Lawn Size | Small to medium | Medium to large |
The operational table demonstrates that self-propelled sweepers provide clear advantages in efficiency and reduced labor, making them particularly suitable for commercial landscaping or large residential properties. Manual sweepers remain advantageous for small, flat lawns where simplicity and low cost are desired.
Maintenance Considerations
Maintenance requirements vary between manual and self-propelled sweepers, influenced by the complexity of their mechanisms. Manual push lawn sweepers generally require basic care: cleaning debris from brushes and collection bags, inspecting wheel integrity, and occasional lubrication of moving parts. Their simplicity reduces the likelihood of mechanical failure and allows straightforward DIY maintenance.
Self-propelled sweepers, however, introduce additional components such as drive chains, gear systems, and speed controls. While these features enhance performance, they also necessitate periodic inspection and maintenance to ensure smooth operation. Lubrication of the drive mechanism, adjustment of gear alignment, and checking wheel traction components are critical to maintaining efficiency. Failure to perform regular maintenance may result in reduced sweeping performance and shorter operational lifespan.
Ergonomics and User Experience
Ergonomics is a key factor in lawn maintenance equipment selection. Manual push lawn sweepers require continuous human effort, which can be physically demanding over extended periods, particularly on large or uneven lawns. Handles are often adjustable to accommodate different user heights, but the user must remain in control of speed and direction at all times.
Self-propelled sweepers significantly improve ergonomics by reducing user exertion. The drive system takes on the majority of propulsion effort, allowing the user to focus primarily on guiding the machine. Some models feature ergonomic handles, speed-adjustable controls, and lightweight designs, contributing to an overall more comfortable operation. This is especially valuable for users with limited physical strength or mobility.
Suitability for Different Lawn Conditions
The choice between manual and self-propelled push lawn sweepers largely depends on lawn size, terrain, and debris type. Manual sweepers perform adequately on small, flat lawns with light debris, offering cost efficiency and ease of storage. However, on large properties, uneven terrain, or lawns with heavy leaf accumulation, self-propelled sweepers are generally preferred for their consistent performance and reduced labor requirement.
Additionally, the type of debris collected influences suitability. Push lawn sweepers with rotating brushes can effectively pick up leaves, grass clippings, and small twigs. Manual sweepers may struggle with wet or dense debris, whereas self-propelled sweepers maintain brush rotation and collection efficiency regardless of minor changes in debris density or moisture content.
Environmental and Cost Considerations
From an environmental perspective, push lawn sweepers offer a sustainable alternative to powered leaf blowers, producing no emissions during operation. Manual models have the lowest environmental footprint, relying entirely on human energy. Self-propelled models, though mechanically assisted, still rely primarily on physical motion rather than combustion engines, maintaining a low environmental impact.
Cost considerations extend beyond initial purchase price. Manual push lawn sweepers are more affordable upfront, with minimal maintenance expenses. Self-propelled sweepers incur higher initial costs and more complex maintenance, but these are offset by reduced labor time and higher operational efficiency, particularly in large or commercial applications.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Manual Push Lawn Sweeper Challenges
- User Fatigue: Prolonged use can be physically demanding. Using shorter sessions or rotating users can alleviate fatigue.
- Limited Terrain Adaptability: Uneven or sloped lawns may reduce efficiency. Ensuring proper brush height adjustment can mitigate this issue.
- Slower Debris Collection: Manual effort may limit coverage. Regular brush inspection and maintenance optimize collection.
Self-Propelled Push Lawn Sweeper Challenges
- Mechanical Complexity: Drive mechanisms require regular maintenance. Following manufacturer maintenance schedules is essential.
- Weight Considerations: Heavier models may be difficult to transport. Choosing a model with folding handles or detachable parts improves portability.
- Higher Cost: Upfront investment is higher, but operational efficiency often justifies the expense over time.
Conclusion
In summary, both manual and self-propelled push lawn sweepers have distinct advantages and limitations. Manual sweepers excel in simplicity, affordability, and suitability for small, flat lawns. Self-propelled sweepers provide enhanced efficiency, reduced labor, and adaptability to challenging terrains, making them ideal for larger lawns or commercial landscaping. Buyers should carefully consider lawn size, terrain type, debris volume, and user capability when choosing between these two options. Understanding these factors ensures optimal performance, user comfort, and long-term satisfaction in lawn maintenance.
FAQ
Q1: Can a manual push lawn sweeper handle wet leaves?
A: Manual push lawn sweepers may struggle with wet leaves because moisture increases debris weight and reduces brush efficiency. Self-propelled models maintain better performance in such conditions.
Q2: How often should I empty the hopper of a push lawn sweeper?
A: Hopper frequency depends on lawn size and debris volume. For large properties, checking the collection bag after every 20–30 minutes of use is recommended.
Q3: Are push lawn sweepers suitable for sloped lawns?
A: Manual sweepers are less effective on steep slopes due to required human force. Self-propelled sweepers with drive assistance perform better on uneven terrain.
Q4: What maintenance is critical for a self-propelled push lawn sweeper?
A: Regular inspection of the drive mechanism, lubrication of gears, brush cleaning, and wheel alignment are essential for optimal performance.
Q5: How long does a push lawn sweeper last?
A: With proper maintenance, both manual and self-propelled sweepers can last several years. Self-propelled models require more frequent mechanical checks.
References
- Lawn Equipment Maintenance and Efficiency Guidelines, National Association of Landscape Professionals, 2024.
- Sustainable Lawn Care Practices, Environmental Lawn Care Journal, 2023.
- Push Lawn Sweepers: Design and Operation Review, International Landscaping Equipment Review, 2022.
NEXT:How does a 40" Plug Aerator differ from a spike aerator?
Interested in cooperation or have questions?

 LANGUAGE
LANGUAGE English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Français
Français


























